Optimization Algorithms
Convex optimization
Gradient descent
Optimization challenges
Common challenges
- local minima
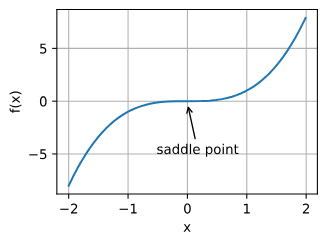
- saddle points
- any location where all gradients of a function vanish but which is neither a global nor a local minimum
Challenges in DL
-
- Almost all optimization problems arising in deep learning are nonconvex
-
Vanishing / Exploding gradients
- Vanishing gradients: the gradients of a neural network's loss function become extremely small, causing the weights to update very slowly and making it difficult for the network to learn effectively
- Exploding gradients: gradients become excessively large, leading to unstable updates and causing the model's parameters to oscillate or diverge during training
How to speed up optimization in DL
- Normalizing inputs
- for tanh: Xavier initialization
- for ReLU: He Initialization
- Gradient checking
- only use in debugging
- remember regularization
- doesn't work for dropout
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Hyperparameter Tuning#Hyperparameter Tuning in Deep Learning
- Batch Normalization
- applies normalization on the inputs of hidden layers
- weakens the coupling between what the early layers parameters have to do and what the later layers parameters have to do. So it allows each layer of the network to learn by itself, a little bit more independently of other layers, and this has the effect of speeding up of learning in the whole network.
- can add a slight regularization effect because of adding noise to hidden layers